Franz Tech Corner News
November, 2013
In this issue
- Success Stories
- SISCOG's CREWS Staff Planning and Management Success Story - Why Lisp and Customer Case Studies
- Just Published - "Principles of Biomedical Informatics, Second Edition", by Ira J. Kalet PhD. - With more Lisp code
- Alstom Smartlock Interlocking
- DATAmaestro - A Unique Data Mining Tool for Industrial Applications
- Design Parametrics - Design Automation
- Japan Lisp Seminar, November 21-22 in Tokyo
- Free Webcast: Augmenting Hadoop for Graph Analytics
- Free Webcast: Taxonomies and Ontologies for Graph Search
- YouTube - The Allegro CL Channel
SISCOG's CREWS Staff Planning and Management Success Story - Why Lisp and Customer Case Studies

SISCOG's CREWS provides solutions to the core problem transportation companies face today - effective planning and management of the work of crew members. CREWS addresses all phases of the planning and management process - long-term planning (duty and roster planning), short-term planning (staff allocation and changes to the plan), real-time management, and controlling the work done. CREWS enables quick and efficient planning and management staff, provides fast responses to train and crew changes, minimises crew-related train disruptions, and provides evaluation of strategic options. A presentation on SISCOG's Lisp applications was given at the ELS'13 conference, the presentation slides are available here .
.
For additional information about SISCOG and CREWS, see here.
Just Published - "Principles of Biomedical Informatics, Second Edition", by Ira J. Kalet PhD. - With more Lisp code
Lisp is the main programing language in this edition, as in the first. It is by far the best for achieving the goals of the book, to present biomedical informatics as a systematic set of formal ideas and methods that are naturally expressed as computations on well-defined representations. In Chapter 1, the basic ideas of symbolic computing are introduced gradually as needed. The Appendix has been expanded to include more tutorial material as well as references to aid the reader who is not so familiar with Lisp. All the code that appears in this book is available at the author's web site at the University of Washington,http://faculty.washington.edu/ikalet/
To read more about this new book, see Principles of Biomedical Informatics, Second Edition
Alstom Smartlock Interlocking

With more than 1,500 installations in over 25 countries, the safety and reliability of the new generation of Alstom's Smartlock electronic interlocking products has more than proven itself. Interfacing with the Automated Train Control (Atlas) system and conventional track equipment (Smartway), Smartlock interlocking guarantees safety for traffic on all types of networks.
To read more about this new application, see Alstrom
DATAmaestro - A Unique Data Mining Tool for Industrial Applications

DATAmaestro® is a powerful cloud predictive analytics tool that will transform your enterprise data from complex problems to working solutions. One multi-dimensional tool to extract, analyze, select, filter, model and report. PEPITe's innovative DATAmaestro combines proven analytic tools with a powerful data management kernel. The business backbone of the product comprises leading data mining technologies, performance management, tailored key performance indicators, and automatic drill-down to solve problems based on facts.
To read more about this new application, see DATAmaestro
Design Parametrics - Design Automation

Design Parametrics is dedicated to bringing to a larger audience the power of knowledge-based engineering through Design++, which lets users capture their engineering and design knowledge for automatic re-use, thus making the computer an active part of the design process rather than a passive tool. Design Parametrics has licensed Design++ technology from Bentley Systems allowing it to develop and distribute Design++ independently. It is also a Bentley partner and provides support to existing Bentley Design++ and PlantWise users.
To read more about this new application, see Design Parametrics
Japan Lisp Seminar, November 21-22 in Tokyo

Please join us for this year's Japan Lisp Seminar, sponsored by Mathematical Systems Inc. and Franz Inc. This is no cost to participate.
For additional information and to register for November 21, see here
For additional information and to register for November 22, see here
Free Webcast: Augmenting Hadoop for Graph Analytics

Wednesday, November 20 - 10:00 AM Pacific
E-commerce sites, auction sites, financial institutions, insurance companies and telephone companies all have event based data that describes transactions between customers (Social Networks) that are located in time and space (GeoTemporal).
All these transactions together form interesting social graphs and patterns of customer behavior. Some of these behaviors are very interesting from a marketing perspective, other behaviors might point to fraudulent actions. Analyzing graphs and geospatial oriented data is notoriously hard to do with typical big data solutions, such as Hadoop, so we use a hyper scalable graph database to do this analysis.
We will present a number of new technologies to make it very straightforward and user friendly to analyze behavioral patterns. We discuss extending SPARQL 1.1 with a large number of magic predicates for geospatial, temporal and social network analysis so that non-specialists can very easily build very powerful queries. We will present new visual discovery capabilities to GRUFF, a graphical user interface for Graph Search. We will demonstrate how users can explore visual graphs and easily turn interesting patterns into SPARQL queries.
To register for this webinar, see http://www.franz.com/ps/services/conferences_seminars/semantic_technologies_v40.lhtml
Free Webcast: Taxonomies and Ontologies for Graph Search
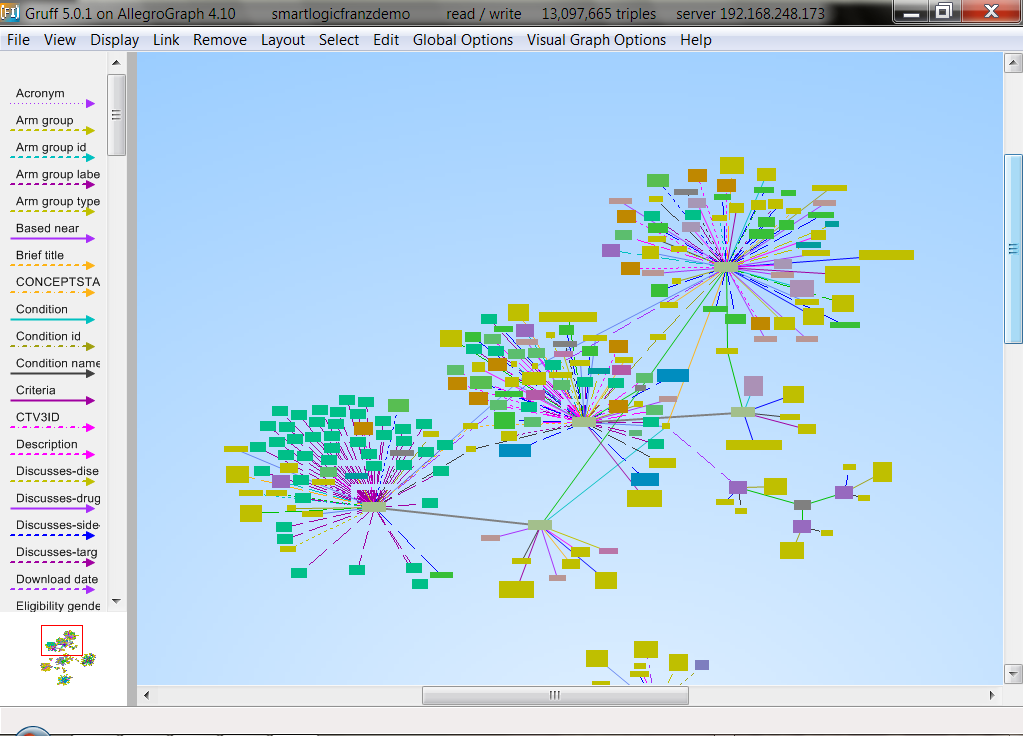
Wednesday, December 11 - 10:00 AM Pacific
Life Science and Healthcare organizations use RDF/SKOS/OWL based vocabularies, thesauri, taxonomies and ontologies to organize enterprise knowledge. There are many ways to use these technologies but one that is gaining momentum is to semantically index unstructured documents through ontologies and taxonomies.
In this talk we will demonstrate two projects where we use a combination of SKOS/OWL based taxonomies and ontologies, entity extraction, fast text search, and Graph Search to create a semantic retrieval engine for unstructured documents.
The first project organized all science related artifacts in Malaysia through a taxonomy of scientific concepts. It indexed all papers, people, patents, organizations, research grants, etc, etc, and created a user friendly taxonomy browser to quickly find relevant information, such as, "How much research funding has been spent on a certain subject over the last 3 years and how many patents resulted from this research".
The second project discusses a large socio-economic content publisher that has millions of documents in at least eight different languages. Reusing documents for new publications was a painful process given that keyword search and LSI techniques were mostly inadequate to find the document fragments that were needed. Fortunately the organization had begun developing a large SKOS based taxonomy that linked common concepts to various preferential and alternative labels in many languages. We used this taxonomy to index millions of document fragments and we'll show how we can perform relevancy search and retrieval based on taxonomic concepts.
To register for this webinar, see http://www.franz.com/ps/services/conferences_seminars/semantic_technologies_v41.lhtml
YouTube - The Allegro CL Channel

Videos covering Allegro CL and related technologies.
Visit the Allegro CL Channel here .
.








 BECOME ALLEGRO CERTIFIED - To obtain your Allegro CL Certification enroll in our LIVE Program which offers developers an opportunity to learn and improve their Lisp programming skills from the comfort of their home or office while interacting with the Franz instructor.
BECOME ALLEGRO CERTIFIED - To obtain your Allegro CL Certification enroll in our LIVE Program which offers developers an opportunity to learn and improve their Lisp programming skills from the comfort of their home or office while interacting with the Franz instructor.


